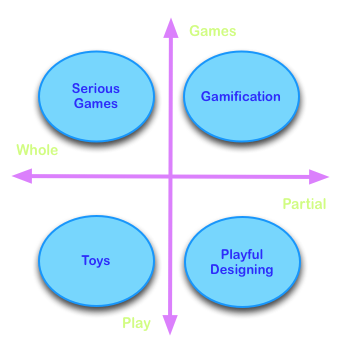
Credit: Diagram by Michelle A. Hoyle
Image: Deterding et al’s (2011) situating of gamification as being partially game-like and being more gaming than playing.
Earlier this summer, I signed up for Coursera’s new gamification course, presented by Kevin Werbach of the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania. In this brief reflection, I consider what makes gamification ‘good’ or ‘bad’ for me. I’ve included links back to the videos I’m referring to here, but you’ll need to be registered with the course in order to view them.
If you know me, you’re probably aware that I generally have a negative opinion of gamification, even though it can be easily and persuasively argued that my research examines how to gamify higher education. My negativity doesn’t stem from the use of game elements or game design techniques in non-game contexts in theory. It arises from the actual implementation.









